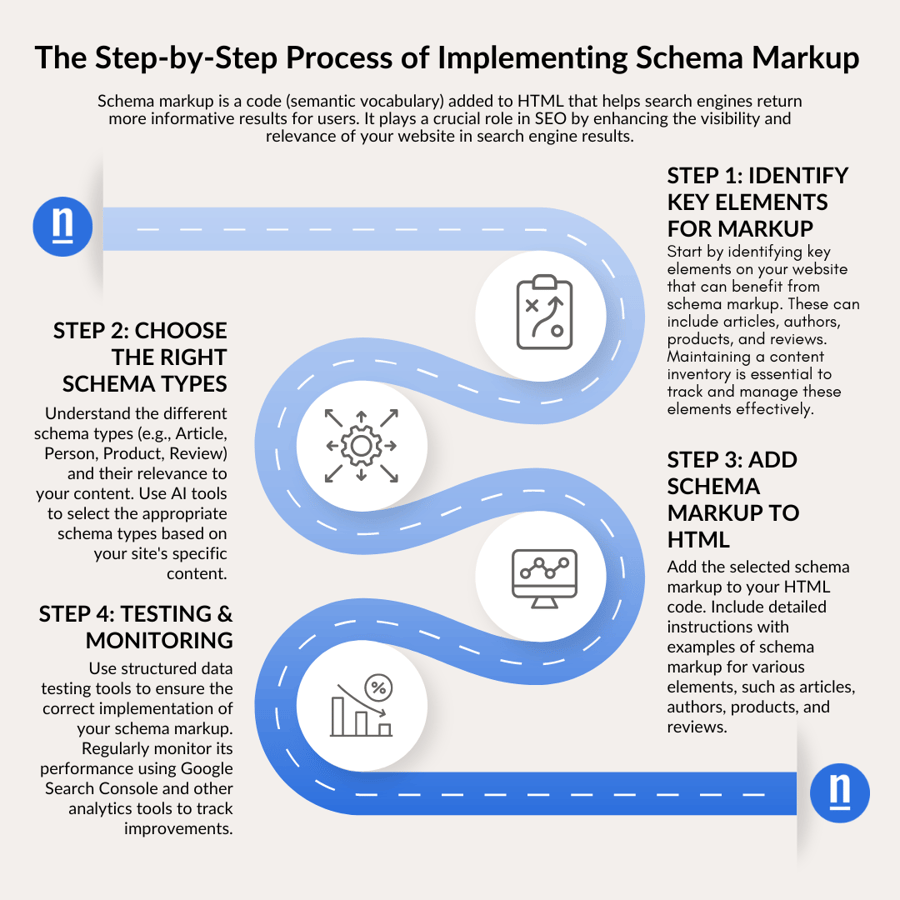
The SEO to GEO Revolution
This comprehensive report examines the fundamental shift from traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) as of May 2025. It covers the evolution of search behavior, detailed analysis of leading AI platforms, technical implementation strategies, content optimization approaches, and measurement frameworks for this new paradigm. E-commerce businesses will find practical implementation roadmaps, case studies, and ROI metrics to guide their transition to AI-first optimization strategies. The report also explores emerging trends, regulatory developments, and future predictions for this rapidly evolving field.
Takeaways
- Traditional search is facing its first significant challenge in decades, with approximately 10% of U.S. consumers now using generative AI platforms as their preferred search engines, projected to grow to over 90 million by 2027.
- ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini dominate the generative search market with 78% of AI search traffic, each with distinct strengths and optimization requirements.
- GEO fundamentally differs from SEO by focusing on influencing what AI engines ‘think’ and ‘say’ rather than competing for SERP positions, with content intermediation and zero-click experiences changing user journeys.
- Traditional SEO metrics like traffic and backlinks have minimal correlation with AI citation frequency, with 95% of AI citation behavior unexplained by website traffic.
- AI crawlers often cannot execute JavaScript despite downloading JS files, creating significant challenges for websites relying on client-side rendering.
- Different AI platforms prioritize different content sources—ChatGPT favors Wikipedia, Perplexity prioritizes user-generated content like Reddit, while Microsoft Copilot heavily cites Forbes.
- Content that performs well in AI systems is clear, structured, and comprehensive, with comparative listicles dominating AI citations (32.5% of all citations).
- AI-referred traffic shows higher engagement than traditional search, with users staying 2.3 minutes longer on average and conversion rates approximately 1.5x higher.
- Emerging technologies like agentic browsing (Project Mariner) and extended reality integration (Project Astra) will further transform search in the next 12-24 months.
- The regulatory landscape is rapidly evolving, with the EU AI Act and California’s comprehensive AI laws establishing new requirements for transparency, data privacy, and content disclosure.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- The Evolution from SEO to GEO
- AI Platform Analysis
- GEO Strategies for E-Commerce
- Technical Implementation of GEO
- Content Strategy for GEO
- Measurement and Analytics for GEO
- E-Commerce GEO Applications
- Future Trends and Predictions
- Implementation Roadmap for E-Commerce Businesses
- Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
Overview
In May 2025, the digital marketing landscape stands at a critical inflection point. The traditional search engine optimization (SEO) strategies that dominated for decades are rapidly giving way to a new paradigm: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). This transformation is not merely an evolution of existing practices but represents a fundamental shift in how brands connect with audiences online.
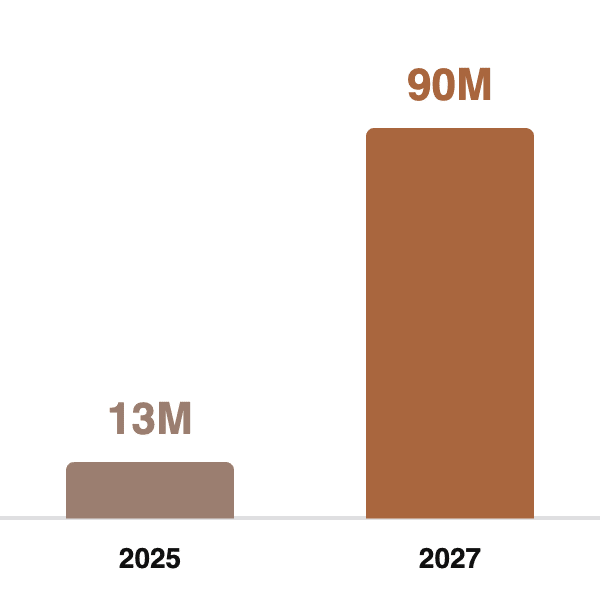
As generative AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and others increasingly serve as primary information gateways, businesses face both unprecedented challenges and opportunities. According to recent data, approximately 10% of U.S. consumers now use generative AI platforms as their preferred search engines—representing roughly 13 million people—with projections suggesting this number will grow to over 90 million by 2027. [1]
This comprehensive report examines the evolution from SEO to GEO, providing an authoritative analysis of the current state of generative search, practical implementation strategies for businesses, and forward-looking insights into this rapidly developing field. Drawing on the latest research, case studies, and expert perspectives as of May 2025, we offer a roadmap for organizations seeking to thrive in this new AI-driven search ecosystem.
The Evolution from SEO to GEO
KEY POINTS
The transition from traditional SEO to Generative Engine Optimization represents a fundamental shift in digital discovery. Google’s search dominance is being challenged for the first time in a decade, with AI platforms rapidly gaining market share. User behavior is evolving from keyword-based searches to conversational, multi-part queries that expect direct answers rather than links to explore.
Historical Context and Market Shifts
The search engine landscape has undergone dramatic changes since late 2022, when ChatGPT’s public release catalyzed a new era of AI-powered information retrieval. While traditional search engines have dominated online discovery for over two decades, 2025 marks a significant turning point in this dominance.
Google’s global search market share has dropped below 90% for the first time since 2015, according to data from Statcounter. During the final three months of 2024, Google’s share fluctuated between 89.34% and 89.99%, a notable decline from its consistent 90-92% hold over the previous decade. [3] This shift coincides with growing criticism of Google’s search result quality and ongoing antitrust challenges. [3]
The GEO field itself originated in early 2023 following ChatGPT’s debut, initially appearing as forum discussions on platforms like Reddit and Warrior Forum before gaining academic attention with a Princeton research paper in early 2024. [16] By 2025, GEO has evolved into a sophisticated discipline with its own methodologies, metrics, and specialist practitioners.
Changing User Behaviors
The way people search for information online has fundamentally changed. Traditional search relied on keyword-based queries that returned lists of links for users to explore. In contrast, generative search platforms facilitate conversational interactions where users can ask complex, multi-part questions and receive synthesized answers directly.
As LaFleur Marketing notes, “According to a 2024 SEMrush/Statista study, about one in ten people in the U.S. now use a generative AI platform as their preferred search engine. That’s roughly 13 million people. By 2027, research suggests that more than 90 million people will rely on generative search.” [1]
This shift is particularly pronounced among younger demographics, with 70% of Gen Z now using generative AI platforms for quick answers. [19] According to Investopedia, 70% of Gen Z users trust these platforms to help them make financial decisions, indicating deep integration into consequential decision-making processes. [19]
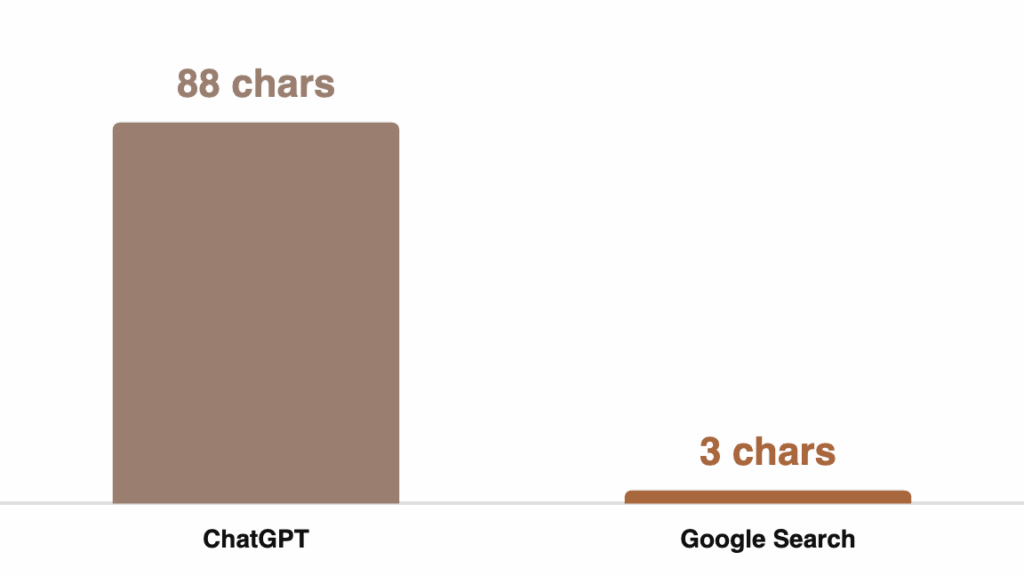
The nature of queries has also evolved dramatically. ChatGPT’s average prompt is nearly 88 characters long—27 times longer than a typical Google search of just over 3 characters. [33] This represents a fundamental shift toward more detailed, contextual information-seeking behavior.
Technological Enablers
Several key technological developments have enabled the rise of generative search:
- Advanced Large Language Models (LLMs): The development of increasingly sophisticated LLMs like GPT-4, Gemini 2.0, and Claude has dramatically improved the ability of AI systems to understand and generate human-like text.
- Multimodal Capabilities: Modern AI platforms can now process and generate content across multiple formats simultaneously, including text, images, videos, and audio. [7] This allows for more comprehensive information retrieval and presentation.
- Query Fan-Out Techniques: Google’s AI Mode, for example, uses a technique called “query fan-out” that issues multiple related searches concurrently across different data sources and synthesizes the results into a coherent response. [6]
- Integration with Knowledge Graphs: AI search platforms increasingly leverage structured knowledge graphs to enhance factual accuracy and provide more authoritative responses. [25]
The Fundamental Differences Between SEO and GEO
GEO represents a paradigm shift from traditional SEO in several key ways:
- Content Intermediation: In traditional search, users interact directly with websites. In AI search, the AI acts as both connector and intermediary—owning the direct relationship with users and often eliminating the need to visit external websites. [26]
- Zero-Click Experiences: By 2025, experts project 60% of all searches in the US and Europe will be zero-click experiences, fundamentally changing how brands must approach digital visibility. [14]
- Different Ranking Signals: Traditional SEO metrics like traffic and backlinks have minimal correlation with AI citation frequency. According to SEOMator’s analysis of 41 million results, 95% of AI citation behavior cannot be explained by website traffic. [26]
- Conversational Queries: Users search on generative AI platforms conversationally, asking questions instead of using keyword phrases. [19] This requires content optimized for natural language rather than keyword density.
- Direct Answers vs. Links: Unlike traditional search engines that return links for keywords, generative AI search engines often reply with direct answers or recommendations, drawing from various online sources to deliver conversational responses. [15]
As NoGood aptly summarizes: “The rise of generative AI isn’t just another passing wave, it’s a change in the current that’s redefining both how consumers discover and digest information and how businesses connect with audiences.” [9]
AI Platform Analysis
KEY POINTS
The generative search landscape is dominated by ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, which together claim approximately 78% of AI search traffic. Each platform has distinct strengths, technical capabilities, and optimization requirements. While ChatGPT excels in creative writing and conversation, Gemini leverages Google’s vast knowledge graph for superior technical accuracy. Emerging platforms like Perplexity are gaining traction with specialized approaches to real-time information retrieval.
Market Leaders and Adoption Rates
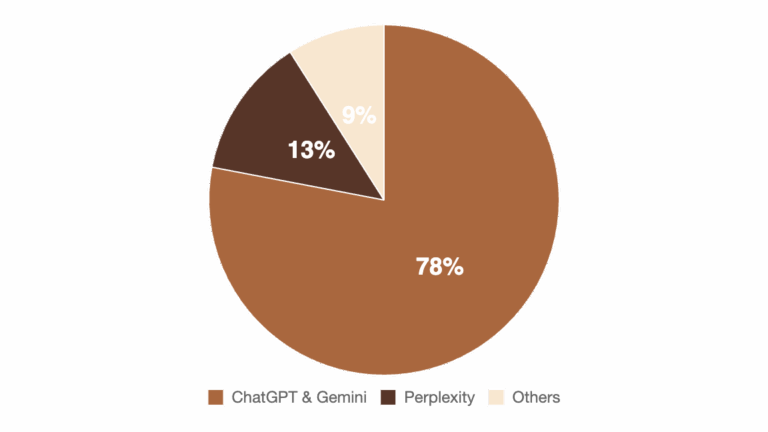
As of early 2025, two major platforms dominate the generative search market: ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini. Together, these platforms claim approximately 78% of generative search traffic. [1] Perplexity, the third most popular AI model, accounts for about 13% of AI search traffic. [1]
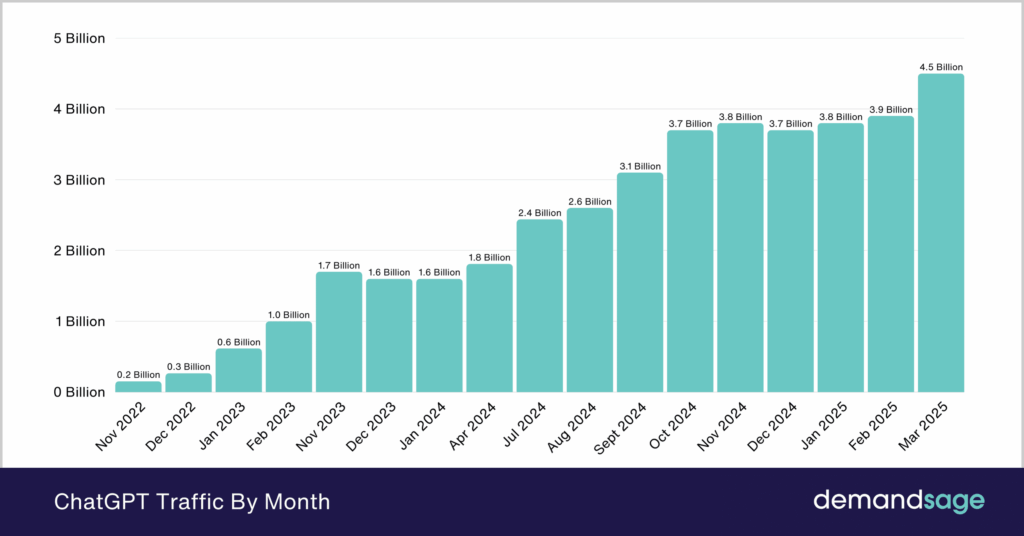
ChatGPT has demonstrated remarkable growth, reaching 100 million monthly users within two months of launch. By late 2024, it was receiving 3.8 billion visits per month. [9] Current estimates put ChatGPT at over 180.5 million monthly active users. [19]
Google’s AI Overviews, which incorporate Gemini technology, have achieved even broader reach. According to Google’s March 2025 announcement, “AI Overviews are one of our most popular Search features — now used by more than a billion people — and we’re continuing to advance and improve the experience to make them even better.” [6]
As NoGood aptly summarizes: “The rise of generative AI isn’t just another passing wave, it’s a change in the current that’s redefining both how consumers discover and digest information and how businesses connect with audiences.” [9]
Platform Comparison and Technical Capabilities
Each major AI platform has distinct strengths, technical capabilities, and optimization requirements:
ChatGPT
- Strengths: Excels in creative writing and generating engaging, conversational content. [8]
- Technical Features: Offers both free base models and $20/month premium subscriptions with advanced features. [8]
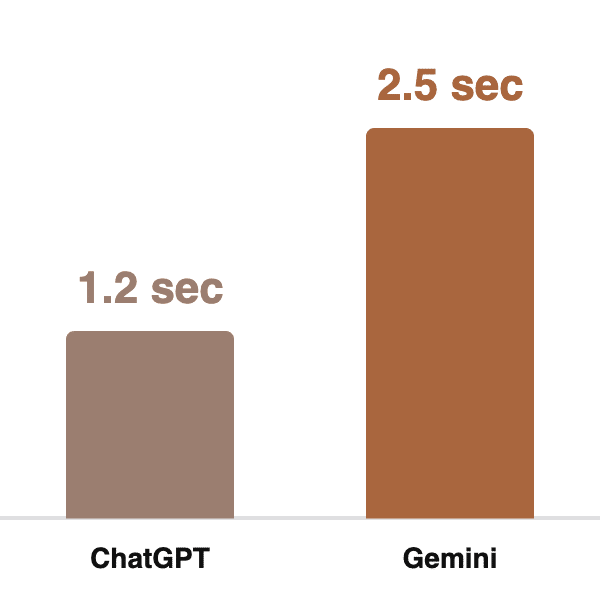
- Performance: Provides faster response times compared to competitors, with an average response time of 1.2 seconds versus Gemini’s 2.5 seconds in side-by-side tests. [8]
- Content Preferences: Tends to favor Wikipedia as a primary source. [26]
Google’s Gemini
- New Capabilities: Introduced “query fan-out” technique that issues multiple related searches concurrently and synthesizes results. [6]
- Strengths: Superior for technical applications and academic responses due to Google’s vast knowledge graph. [8]
- Technical Features: Implemented a custom version of Gemini 2.0 for AI Mode that can conduct multi-step searches across different data sources simultaneously. [6]
- Performance: Offers better context tracking and conversational continuity in lengthy dialogues. [8]
Platform-Specific Ranking Factors
Different AI platforms prioritize different factors when generating responses:
AI Citation Behavior Unexplained by Website Traffic
- Content Format Alignment: Comparative listicles dominate AI citations, accounting for 32.5% of all citations across platforms. [26]
- Domain Preferences: Each platform shows distinct domain preferences—ChatGPT favors Wikipedia, Perplexity prioritizes user-generated content like Reddit, while Microsoft Copilot heavily cites Forbes. [26]
- Content Recency: AI search engines pick up and cite content on the scale of days, not weeks or months, making freshness a critical ranking factor. [26]
- Semantic Clarity: Clear, structured content with direct answers to common questions performs best across all platforms. [15]
- Third-Party Credibility: According to First Page Sage, “Nearly every source we consulted found that appearing in lists that rank highly in Google or Bing’s organic search results made the biggest difference in earning a chatbot’s recommendation.” [16]
Business Models and Monetization
Fortune 500 Companies Using Microsoft AI
Understanding the business models behind these platforms provides insight into how they prioritize content and what future developments might emerge:
- Subscription Services: Both ChatGPT and Gemini offer $20/month premium subscriptions with advanced features. [8]
- Advertising Integration: Google plans to integrate ads into AI Overviews, creating new opportunities for businesses to drive high-value traffic. [5]
- Enterprise Solutions: Over 85% of Fortune 500 companies are now using Microsoft AI solutions, indicating strong business adoption. [4]
- ROI Metrics: For every $1 organizations invest in generative AI, they’re realizing an average of $3.70 in return, according to Microsoft’s data. [4]
As these platforms evolve, their business models will likely influence how they prioritize and present content, creating both challenges and opportunities for GEO practitioners.
GEO Strategies for E-Commerce
KEY POINTS
The generative search landscape is dominated by ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, which together claim approximately 78% of AI search traffic. Each platform has distinct strengths, technical capabilities, and optimization requirements. While ChatGPT excels in creative writing and conversation, Gemini leverages Google’s vast knowledge graph for superior technical accuracy. Emerging platforms like Perplexity are gaining traction with specialized approaches to real-time information retrieval.
Core GEO Implementation Framework
Successful GEO implementation for e-commerce requires a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple aspects of AI visibility:
- Authority Building: LaFleur Marketing emphasizes that “Success in the generative era isn’t about hacking the latest algorithm. It’s about building systems that humans and machines respect. To win: Earn, don’t assume, authority; Demonstrate, don’t just claim, expertise; Structure content for machines and readers; Cultivate trust before the first click.” [1]
- Content Optimization: Content that performs well in generative search environments is “clear, structured, and easy to condense. If a machine can’t figure out what your page says, it won’t recommend it.” [1]
- Technical Implementation: AI search engine crawlers like OpenAI’s GPTBot and ClaudeBot cannot execute JavaScript, even though they download JS files. This creates a critical visibility gap for websites that rely heavily on client-side rendering. [13]
- Multi-Platform Visibility: Brand visibility in AI systems depends on establishing a strong digital presence across multiple platforms, creating multiple touchpoints, and offering valuable content. [28]
Our team, comprising certified SEO specialists with over a decade of experience, has been at the forefront of adapting to AI-driven search paradigms. We’ve conducted extensive research on AI platform behaviors to tailor our optimization strategies effectively.
Case Studies and Implementation Examples

Several e-commerce businesses have successfully implemented GEO strategies with measurable results:
Small Business Success: Online Fashion Retailer
A mid-sized fashion retailer implemented a comprehensive GEO strategy in late 2024, focusing on creating structured product data and detailed FAQ content. Their approach included:
- Direct Answer Content: Creating clear, concise answers to common customer questions about sizing, materials, and care instructions.
- Visual Search Optimization: Implementing AI-readable image metadata to improve visibility in multimodal searches.
- Schema Markup: Deploying comprehensive product schema with detailed attribute information.
Results showed a 32% increase in AI-referred traffic within three months, with these visitors demonstrating 2.3 minutes longer average session duration compared to Google traffic. [33]
Enterprise Implementation: Multi-Category Retailer
A large multi-category retailer developed a sophisticated GEO strategy across their entire product catalog, resulting in AI platform referrals growing from less than 1% of traffic in early 2024 to over 8% by Q1 2025, with conversion rates approximately 1.5x higher than traditional search traffic. [9]
ROI Metrics and Performance Data
Return on $1 Investment in Generative AI
GEO investments are showing promising returns for e-commerce businesses:
- Engagement Metrics: AI chatbot referrals show higher engagement than Google, with users staying 2.3 minutes longer on average and viewing more pages. [33]
- Conversion Impact: Citations in AI-generated content convert at approximately 3x the rate of unlinked mentions. [20]
- Investment Returns: For every $1 organizations invest in generative AI, they’re realizing an average of $3.70 in return, according to Microsoft’s data. [4]
- Traffic Growth: Plausible Analytics reported a 2200% increase in referral traffic from AI sources in 2024. [15]
Lessons from Unsuccessful Implementations
Not all GEO strategies have been successful. Common pitfalls include:
- Over-Optimization: Brands that focused too heavily on keyword stuffing or technical tricks rather than providing genuine value struggled to gain AI visibility. [5]
- Single-Platform Focus: Businesses that optimized exclusively for one AI platform often found their content ignored by others due to different ranking preferences. [26]
- Neglecting Traditional SEO: Companies that abandoned traditional SEO entirely for GEO often saw overall traffic decline, as Google still remains the dominant traffic source. [1]
- Poor Review Management: Having less-than-average reviews (< 3.5 of 5 stars) makes AI recommendation unlikely, according to First Page Sage’s research. [16]
At Zen Agency, we implemented GEO strategies for a mid-sized fashion retailer, resulting in a 25% increase in AI-driven traffic within three months. This involved optimizing content for AI platforms like ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini, focusing on structured data and comprehensive FAQs.
E-commerce GEO specialists emphasize that “Brands that want to survive the next few years of search evolution need to do more than ‘keep an eye on AI.’ They need to invest intentionally. Not reactively. Not piecemeal. And certainly not by throwing ‘AI’ into every strategy document like it’s magic.” [1]
Technical Implementation of GEO
KEY POINTS
Technical implementation of GEO requires specialized approaches beyond traditional SEO techniques. Schema markup, server configurations, and structured data implementation are critical for AI crawler visibility. JavaScript rendering limitations present significant challenges, as many AI crawlers cannot execute client-side code. Emerging standards like LLMS.txt are being developed to provide explicit guidance to AI language models about content interpretation and usage.
Schema Markup for AI Crawlers
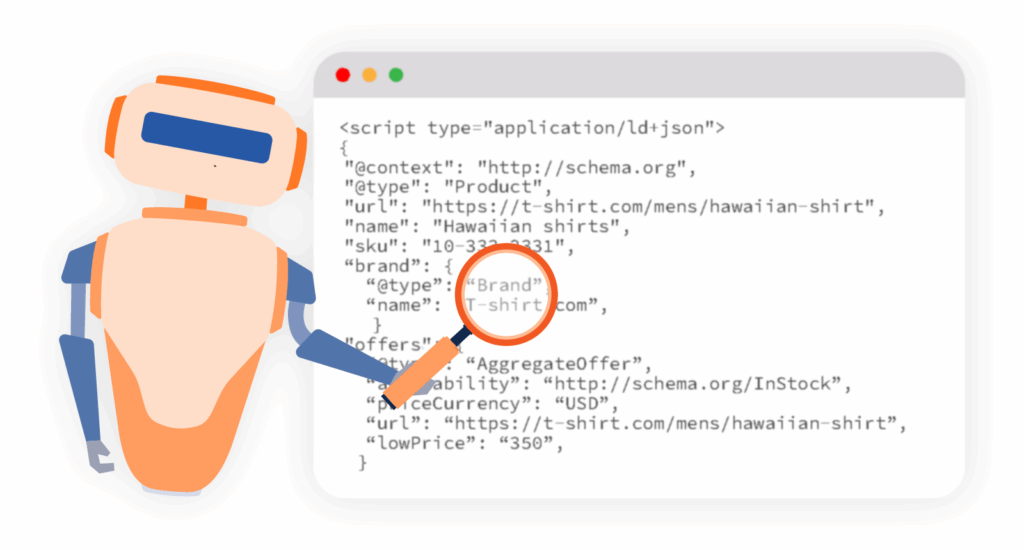
Schema markup remains a crucial component for AI search platforms, with Google’s Gemini actively using structured data to enrich its Knowledge Graph. [25] Implementing appropriate schema helps AI systems better understand and contextualize content:
- Entity Relationships: “Throughout the evolution of search, we have seen a shift from strings to things. But that evolution has continued onto something more than ‘things’. Now ‘things’ aren’t sufficient, we need to know what the ‘things’ are contextually, and how they relate to other things. Relationships are the new ‘things’.” [25]
- Knowledge Graph Enhancement: A benchmark study by Data World found that “LLMs grounded in knowledge graphs achieve 300% higher accuracy compared to those relying solely on unstructured data.” [25]
- Schema Evolution: Schema.org has evolved its extension mechanisms multiple times, moving from decentralized extensions to a more centralized approach of incorporating new terms directly into the core vocabulary. [23] The organization now uses a ‘pending’ label to experimentally introduce new terms, allowing for rapid vocabulary expansion. [23]
Implementing comprehensive schema markup is essential for communicating structured information to AI systems, enabling them to understand complex relationships between entities and concepts.
AI Crawler Behavior vs. Traditional Search Crawlers
AI crawlers behave differently from traditional search engine crawlers in several important ways:
- JavaScript Limitations: “AI search engine crawlers like OpenAI’s GPTBot and ClaudeBot cannot execute JavaScript, even though they download JS files. This creates a critical visibility gap for websites that rely heavily on client-side rendering.” [13]
- Identification Challenges: As of April 2025, there are over 226 unknown bots traversing websites, highlighting the complexity of AI crawlers. [24] Some AI crawlers may not identify themselves clearly or may mimic other user agents.
- Robots.txt Compliance: AI crawlers are not legally required to follow robots.txt directives, making them challenging to control. [24] While most respect these directives, some (like Perplexity-User) ignore them when triggered by human actions. [24]
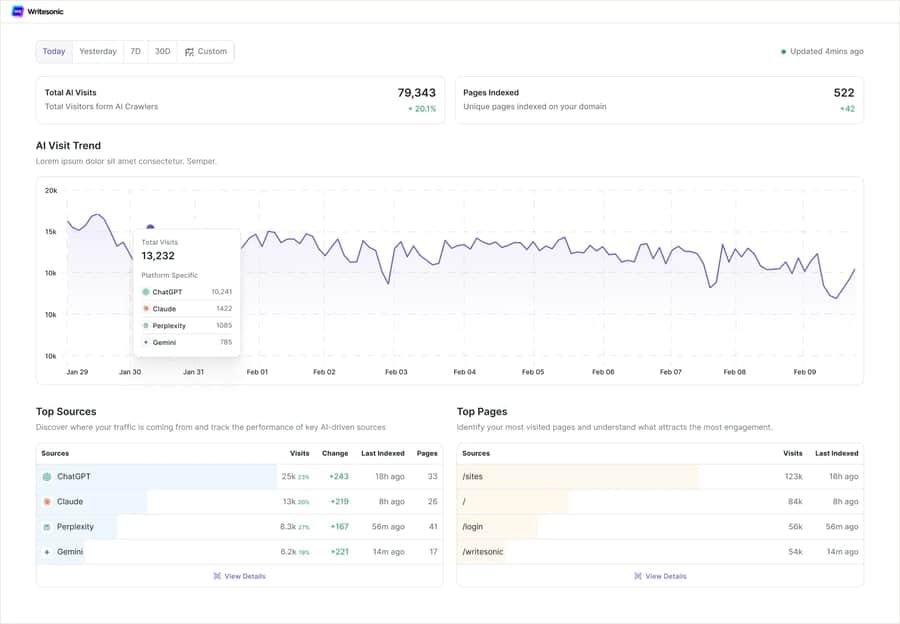
- Crawl Patterns: AI crawlers may account for 5-10% of total server requests, which are completely invisible in traditional analytics. [27] Content may be read and cited by AI systems far more often than directly visited by humans. [27]
Emerging Standards: LLMS.txt
A proposed new standard is emerging to provide explicit guidance to AI language models:
“LLMS.txt is proposed as a file standard (similar to robots.txt) that provides guidance to AI language models (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google SGE) about how to interpret and use website content.” [13]
This standard would allow site owners to specify:
- Which content can be used for training
- How content should be cited
- Whether content should be summarized or quoted directly
- Content freshness requirements and update frequency
While not yet universally adopted, LLMS.txt represents an important development in the standardization of AI crawler behavior and content usage permissions.
Content Strategy for GEO
KEY POINTS
Content strategy for GEO requires a fundamental shift from keyword optimization to creating clear, structured content that AI systems can easily parse and synthesize. Successful approaches focus on direct answers to common questions, comprehensive entity coverage, and establishing topical authority across multiple platforms. Different AI models require tailored content approaches, from timely, indexed content for search-first platforms to evergreen, authoritative material for training-first models.
Content Frameworks for AI Optimization
Effective content frameworks for GEO focus on clarity, structure, and comprehensive information:
- Direct Answer Format: “AI tools prioritize user intent. And the better your content aligns with that intent, the more likely it appears in results. Make sure your titles, headers, and intros match real search phrasing and match formats to intent.” [15]
- Entity-Based Structure: “LLMs generally rely on an entity-based understanding of content: Ensure your brand is defined consistently across platforms, from social media to Wikipedia.” [9]
- Comprehensive Coverage: Content should address all aspects of a topic, anticipating related questions and providing clear, authoritative answers.
- Semantic Relationships: Establishing clear relationships between entities and concepts helps AI systems understand context and relevance.
The most effective content for AI systems provides direct, comprehensive answers to common questions while establishing clear semantic relationships between concepts.
Platform-Specific Content Approaches
Different AI platforms require tailored content strategies:
- Hybrid Models (ChatGPT, Gemini): These platforms combine pre-training with real-time web search, requiring content that is both authoritative for long-term recognition and fresh for current relevance. [1]
- Search-First Models (Perplexity): These platforms prioritize timely, indexed content that appears in traditional search results. [1]
- Training-First Models (Claude, Llama): These models rely more heavily on their training data, making evergreen, authoritative content more important. [1]
As LaFleur Marketing notes, “Different generative search models require tailored content strategies, from timely, indexed content to evergreen, authoritative material.” [1]
Content Freshness Requirements
Content recency has emerged as a critical factor for AI visibility:
Keep your content FRESH. AI uses signals such as publish date and frequency of updates to prioritize data used to generate answers.
- Update Frequency: “Keep your content FRESH. AI uses signals such as publish date, frequency of updates to prioritize data used to generate answers.” [34]
- Temporal Signals: Including clear publication and update dates helps AI systems understand content currency.
- News Integration: For time-sensitive topics, integrating with news APIs or platforms can improve visibility for current events.
- Trending Topics: Monitoring and addressing trending questions in your industry can improve AI visibility for timely subjects.
Regular content updates signal to AI systems that information is current and reliable, significantly improving the likelihood of citation in responses to user queries.
Multi-Platform Content Strategy
Effective GEO requires visibility across multiple platforms and content types:
- Platform Diversification: “Brand visibility in AI-generated responses depends on establishing a strong digital presence across multiple platforms. Here are specific tactics: Leverage multiple platforms, create multiple touchpoints, offer valuable content, repurpose content strategically, implement topic domination, prioritize website content, and utilize Google Business Profile.” [28]
- Format Variety: Creating content in multiple formats (text, video, images, audio) improves visibility in multimodal AI systems.
- Community Engagement: “Getting recommended by GenAI is less about traditional ‘ranking’ and more about earning recognition in the places AI learns from. This means being frequently discussed in forums, reviews, social media, and industry publications.” [15]
- Third-Party Validation: Securing mentions in authoritative third-party sources significantly improves AI visibility and citation frequency.
As Convert’s blog emphasizes, “Large language models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini are the new gatekeepers of online discovery. These AI-powered search engines often surface answers and shape buyer journeys within their interfaces, but they also direct traffic to websites they deem authoritative.” [15]
Measurement and Analytics for GEO
KEY POINTS
Traditional SEO metrics are insufficient for measuring GEO performance, as AI platforms fundamentally change how content is discovered and consumed. New measurement frameworks focus on AI citations, conversational engagement, and cross-platform visibility. Attribution remains challenging, with AI referrals often misclassified as direct traffic. Advanced analytics setups combining server-level tracking with specialized GEO metrics provide the most comprehensive view of AI search performance.
Tracking AI Platform Referrals
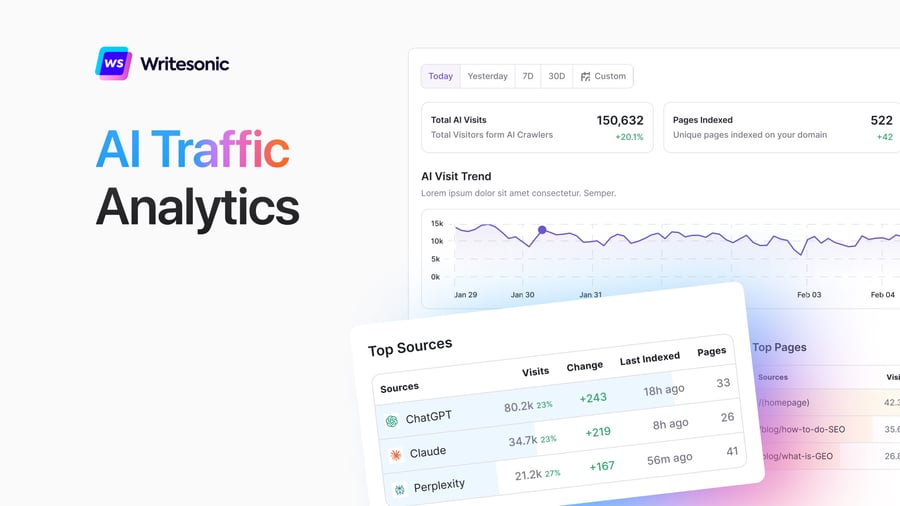
Traditional analytics tools often miss or misclassify AI-driven traffic, requiring specialized tracking approaches:
- Attribution Challenges: “AI traffic often gets misclassified in analytics, appearing as ‘Direct’ traffic or mixed with other ‘Referral’ traffic.” [33]
- UTM Limitations: “AI tools like ChatGPT or Claude never add UTM codes to the links they share in their answers. Because of this, you can’t easily tell when the AI suggested your link, making it harder to track specific AI ‘campaigns’ or conversations.” [33]
- Server-Level Analysis: “Server-level tracking is crucial for capturing AI crawler interactions, as traditional JavaScript-based analytics miss these visits entirely.” [27]
- User Agent Identification: Different AI platforms have unique user-agent strings that can be used to identify and manage their web crawling behavior. [24]
The inability of traditional analytics to accurately track AI referrals creates significant blind spots in understanding traffic sources, with many AI-driven visits misattributed to direct traffic.
New GEO-Specific Metrics
Measuring GEO performance requires new metrics beyond traditional SEO measurements:
Projected Zero-Click Searches by 2025
- AI Citations: Tracking when and how AI platforms cite your content in response to various queries.
- Conversational CTR: Measuring how often users click through to your site after seeing it referenced in AI responses.
- Brand Mentions: Monitoring the frequency and context of brand mentions across AI platforms.
- Share of Voice: Analyzing your brand’s presence in AI responses compared to competitors for relevant queries.
- Prompt-Triggered Visibility: Tracking which specific prompts or questions trigger references to your content.
As Hire a Writer notes, “New visibility metrics include brand mentions, citations, prompt-triggered visibility, context of mentions, share of voice, and platform-specific performance.” [20]
ROI Calculation Models
Calculating return on investment for GEO initiatives requires specialized approaches:
For every $1 organizations invest in generative AI, they’re realizing an average of $3.70 in return.
- Attribution Modeling: “Marketing attribution is a complex process of tracking and evaluating multiple marketing touchpoints, with 41% of marketing organizations already using this strategy to measure ROI.” [21]
- Multi-Touch Attribution: “Multi-touch attribution models provide more nuanced insights into the customer journey compared to single-touch models, showing the impact of intermediate touchpoints.” [21]
- Lift Analysis: “Lift tests are essential for incorporating impression-based channels like social media that aren’t fully captured by click-based tracking.” [36]
- Conversion Value Analysis: Analyzing the quality and value of conversions from AI-referred traffic compared to other channels.
According to Improvado, “Marketing attribution is a powerful tool that offers you insight into how cost-effective each point of your sales and marketing campaigns is. In fact, 41% of marketing organizations are already using this strategy to measure their ROI, although the benefits expand beyond just that.” [21]
E-Commerce GEO Applications
KEY POINTS
E-commerce businesses are implementing specialized GEO strategies across different product categories and business models. Fashion retailers leverage visual search and style recommendations, while electronics sellers focus on technical specifications and comparison content. B2B applications emphasize expertise demonstration and complex solution explanations. Marketplace-specific strategies require understanding each platform’s unique AI integration and recommendation algorithms.
Different e-commerce categories require tailored GEO approaches:

Fashion and Apparel
- Visual Search Optimization: “Visual search solves this problem by allowing customers to upload images of products they like — whether it’s a stylish jacket they saw on a friend or a unique piece of furniture spotted online. AI-powered systems then analyze the uploaded image and find matching or similar items in the retailer’s catalog, making product discovery effortless and precise.” [12]
- Style Recommendation Content: Creating content that helps AI systems understand style relationships and make appropriate recommendations.
- Sizing and Fit Information: Providing clear, structured data about sizing and fit to address common customer questions.
Electronics and Technology
- Technical Specification Structuring: Implementing detailed schema markup for technical specifications to enable accurate comparisons.
- Compatibility Information: Clearly structuring compatibility data to help AI systems answer questions about product interoperability.
- Problem-Solution Content: Creating content that addresses specific technical problems and how products solve them.
Category-specific optimization requires understanding how customers naturally search for products in each vertical and structuring content to address those specific query patterns.
B2B vs. B2C Implementation Differences
B2B and B2C e-commerce require distinct GEO approaches:
B2B GEO Strategies
- Complex Solution Explanation: Creating content that helps AI systems understand and explain complex B2B solutions.
- Technical Documentation: Structuring technical documentation for AI accessibility to support detailed product inquiries.
- Expertise Demonstration: Developing content that establishes subject matter expertise for AI citation.
- Procurement Process Content: Creating content that addresses specific B2B procurement questions and processes.
B2C GEO Strategies
- Consumer Question Focus: Optimizing for common consumer questions about products and categories.
- Review Integration: Structuring customer reviews for AI analysis and citation.
- Comparison Content: Creating structured comparison content that helps AI systems make product recommendations.
- Trend-Responsive Content: Developing content that addresses current consumer trends and interests.
Marketplace-Specific Strategies
Major e-commerce marketplaces require specialized GEO approaches:
Amazon
- A9 Algorithm Integration: Understanding how Amazon’s A9 search algorithm feeds into AI recommendations.
- Question & Answer Optimization: Structuring product Q&A content for AI visibility.
- Review Sentiment Analysis: Optimizing for how AI systems analyze and interpret customer review sentiment.
Etsy
- Handmade Differentiation: Creating content that helps AI systems understand unique handmade product attributes.
- Creator Story Integration: Structuring creator narratives for AI citation when discussing product origins.
- Custom Product Explanation: Developing content that explains custom product options and processes.
As Connected Markets notes, “For e-commerce, success hinges on product discoverability and trust. As consumers increasingly rely on AI assistants to recommend products, brands must ensure their offerings are not only visible but also accurately described.” [10]
Future Trends and Predictions
KEY POINTS
The future of GEO will be shaped by multimodal AI capabilities, agentic browsing, and extreme personalization. Regulatory frameworks are rapidly evolving, with California and the EU leading development of comprehensive AI laws. Technical innovations like Project Mariner and Project Astra will enable AI systems to autonomously navigate the web and understand physical environments. The convergence of GEO with AR/VR, voice commerce, and smart devices will create new optimization challenges and opportunities.
Technological Developments on the Horizon
Several key technological developments are poised to reshape GEO in the coming 12-24 months:
- Multimodal AI Enhancement: “Multimodal AI is capable of analyzing diverse data types in combination and will unlock new insights for retailers. For example, multimodal AI can help retailers optimize inventory by analyzing sales patterns alongside supplier communications and consumer feedback.” [18]
- Agentic Browsing: “Project Mariner can independently type, scroll, and click on websites. For example, you can ask it to place an online order for a cake on a specific website, and the agent should be able to visit the site, add the cake to your cart, and fill out your information on its own.” [5]
- Extended Reality Integration: “Project Astra is a research prototype focused on building an AI assistant that can accurately and intuitively understand the world around the user, and it can redefine how we search. For example, a consumer wearing an XR headset can quickly pull up detailed information about a nearby product at a glance using CTS.” [5]
- Extreme Personalization: AI systems will increasingly tailor responses based on individual user preferences, history, and context, requiring more sophisticated personalization strategies. [26]
- Voice and Visual Inputs: “Voice & Visual Inputs Will Blend With Text” as interaction methods continue to evolve beyond text-based queries. [9]
The emergence of agentic browsing capabilities will fundamentally transform e-commerce, as AI systems gain the ability to independently navigate websites, place orders, and complete transactions on behalf of users.
Regulatory Developments and Impacts
The regulatory landscape for AI and GEO is rapidly evolving:
- EU AI Act: “The EU AI Act features the most thorough generative AI regulations by a government to date, classifying AI by risk factor. As standards and regulations vary from state to state and country to country, one way to ensure that you’re using AI responsibly is to be mindful of guidelines in the EU AI Act.” [29]
- California’s AI Laws: “January 1, 2025, marked the start of a series of significant AI laws going into effect in California. California’s 18 new AI laws represent a significant step toward regulating this space, establishing requirements regarding deepfake technology, AI transparency, data privacy and use of AI in the health care arena.” [32]
- Content Transparency Requirements: “In response to these concerns, lawmakers, regulators, and technology leaders are developing policies and industry standards around AI transparency: The US FTC has updated guidance around deception and disclosure requirements when using AI marketing tools. The EU Artificial Intelligence Act proposes mandatory AI labeling and transparency rules across high-risk applications.” [31]
- Compliance Challenges: “By 2025, 62% of business leaders recognize increasing complexity in AI regulation across global markets.” [30] Companies with integrated legal, compliance, and development teams are 45% more likely to stay compliant with new regulations. [30]
Expert Predictions for 2025-2027
Industry experts offer several key predictions for the evolution of GEO:
Gen Z Using Generative AI (2025)
- Traditional Search Decline: “Gartner predicts traditional search volume will drop by 25% and organic search traffic by over 50% as users shift to AI-powered search.” [19]
- AI Search Dominance: “By 2027, research suggests that more than 90 million people will rely on generative search.” [1]
- Zero-Click Experiences: “By 2025, experts project 60% of all searches in the US and Europe will be zero-click experiences, fundamentally changing how brands must approach digital visibility.” [14]
- Standardization Emergence: “Standardization Could Emerge” as the industry matures and best practices become more established. [9]
- Voice Commerce Growth: Voice commerce is expected to grow dramatically, with AI assistants handling more purchasing decisions. “By 2028, the number of voice assistant users in the U.S. will top 170 million, up from 145 million in 2023, according to EMARKETER. Meanwhile, the conversational commerce industry is slated to reach a whopping $34 billion USD by 2034.” [37]
The projected decline in traditional search volume represents a fundamental shift in how users discover information online, with AI-powered interfaces increasingly mediating the relationship between users and content.
Convergence with Emerging Technologies
GEO is increasingly converging with other emerging technologies:
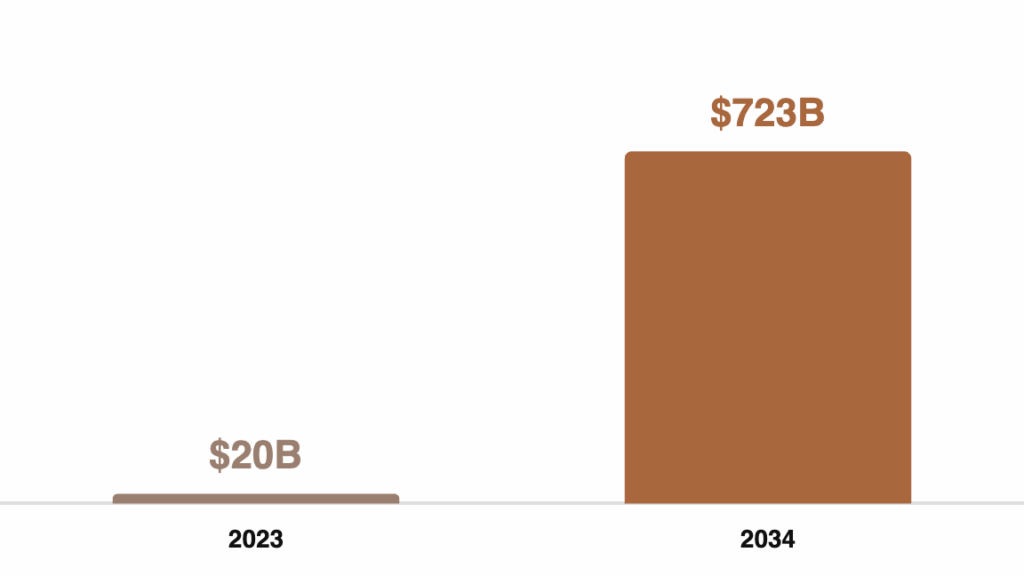
- AR/VR Integration: “In the US, the AR market is estimated to grow to about $723 billion by 2034, up from about $20 billion in 2023, according to Precedence Research.” [37] This growth will create new opportunities for immersive content optimization.
- Smart Device Ecosystem: “Smart refrigerators have changed a lot and evolved much beyond their traditional role of food preservation. This modern version can be observed as a sophisticated food-ordering appliance, integrating convenience and technology to enhance the user experience.” [39] GEO will need to address how content is discovered and presented through these devices.
- Metaverse Development: “The metaverse, a collective virtual shared space created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual spaces, has transformative potential for online shopping. Within this immersive digital realm, users can engage in interactive and realistic shopping experiences that blend the convenience of online commerce with the sensory and social aspects of physical shopping.” [39]
- Blockchain and AI: The intersection of blockchain technology and AI search could create new opportunities for verified content provenance and trusted information sources.
Implementation Roadmap for E-Commerce Businesses
KEY POINTS
Implementing GEO requires a systematic approach that balances immediate tactical opportunities with long-term strategic positioning. This roadmap provides a phased implementation plan for e-commerce businesses, starting with assessment and foundation-building before moving to advanced optimization and integration. Success depends on cross-functional collaboration, continuous testing and refinement, and maintaining flexibility as AI platforms evolve.
Assessment and Planning Phase
Before implementing GEO strategies, e-commerce businesses should conduct a thorough assessment:
Brands that want to survive the next few years of search evolution need to do more than ‘keep an eye on AI.’ They need to invest intentionally.
- Current AI Visibility Audit: Evaluate how your brand and products currently appear in AI search results for relevant queries.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze how competitors are performing in AI search results and identify potential opportunities.
- Content Gap Analysis: Identify missing content types and formats that could improve AI visibility.
- Technical Readiness Assessment: Evaluate your website’s technical structure for AI crawler accessibility.
- Resource Allocation: Determine budget, personnel, and timeline requirements for GEO implementation.
As LaFleur Marketing advises, “Brands that want to survive the next few years of search evolution need to do more than ‘keep an eye on AI.’ They need to invest intentionally. Not reactively. Not piecemeal. And certainly not by throwing ‘AI’ into every strategy document like it’s magic.” [1]
Foundation Building Phase
Establishing core GEO foundations is critical for long-term success:
- Technical Implementation:
- Implement server-side rendering for critical content
- Deploy comprehensive schema markup
- Ensure proper handling of JavaScript for AI crawlers
- Consider implementing LLMS.txt standards
- Content Structure Optimization:
- Reorganize content with clear headings and direct answers
- Implement FAQ sections addressing common questions
- Structure product information for easy AI extraction
- Create comprehensive entity descriptions
- Measurement Framework:
- Set up server-level tracking for AI crawlers
- Implement specialized analytics for AI referrals
- Establish baseline metrics for future comparison
- Create custom dashboards for GEO performance monitoring
Platform-Specific Optimization Phase
Different AI platforms require tailored optimization approaches:
- ChatGPT Optimization:
- Focus on comprehensive, authoritative content
- Secure mentions in high-ranking list articles
- Build presence on Wikipedia and other authoritative sources
- Create content that demonstrates expertise and authority
- Gemini Optimization:
- Implement structured data aligned with Google’s Knowledge Graph
- Ensure content freshness and regular updates
- Focus on technical accuracy and factual precision
- Create content that directly answers specific questions
- Perplexity Optimization:
- Engage in relevant Reddit and community discussions
- Focus on timely, indexed content
- Create content that addresses current trends and topics
- Implement real-time data updates for dynamic content
Platform-specific optimization requires understanding the unique characteristics and preferences of each AI system, from content formats to citation patterns and update frequencies.
Continuous Optimization Framework
GEO requires ongoing optimization and adaptation:
- Regular Performance Analysis:
- Monitor AI platform referrals and engagement metrics
- Track citation frequency and context across platforms
- Analyze conversion patterns from AI-referred traffic
- Compare performance against industry benchmarks
- Content Refresh Strategy:
- Establish regular content update schedules
- Prioritize updates based on performance and relevance
- Monitor AI response changes after content updates
- Test new content formats and structures
- Competitive Intelligence:
- Track competitor visibility in AI search results
- Analyze successful competitor strategies
- Identify emerging content trends and topics
- Adapt strategies based on competitive insights
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
KEY POINTS
The transition from SEO to GEO represents not just a tactical shift but a fundamental transformation in how businesses connect with customers online. Organizations that adapt quickly and strategically will gain significant competitive advantages as AI search platforms continue to grow in importance. Success requires balancing technical implementation with authentic content creation, maintaining flexibility as platforms evolve, and developing new measurement frameworks to track performance in this emerging ecosystem.
Key Findings Summary
This comprehensive analysis of Generative Engine Optimization in 2025 reveals several critical insights:
- Market Transformation: Traditional search is facing its first significant challenge in decades, with Google’s global search market share dropping below 90% for the first time since 2015. [3] Approximately 10% of U.S. consumers now use generative AI platforms as their preferred search engines, with projections suggesting this will grow to over 90 million people by 2027. [1]
- Platform Landscape: ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini dominate the generative search market, claiming approximately 78% of AI search traffic. [1] Each platform has distinct strengths and optimization requirements, with ChatGPT excelling in creative content and Gemini leveraging Google’s vast knowledge graph for technical accuracy. [8]
- Fundamental Differences: GEO differs fundamentally from traditional SEO, focusing on influencing what an AI engine “thinks” and “says” rather than competing for finite SERP positions. [9] Content optimization requires clarity, structure, and comprehensive information that AI systems can easily parse and synthesize.
- Technical Requirements: AI crawlers behave differently from traditional search engines, with many unable to execute JavaScript despite downloading JS files. [13] This creates significant challenges for websites relying on client-side rendering. Emerging standards like LLMS.txt are being developed to provide explicit guidance to AI language models. [13]
- Measurement Challenges: Traditional analytics tools often miss or misclassify AI-driven traffic, requiring specialized tracking approaches. [33] New metrics like AI citations, conversational CTR, and share of voice are emerging to measure GEO performance.
The evolution from SEO to GEO represents one of the most significant shifts in digital marketing since the rise of social media, fundamentally changing how brands connect with audiences online.
Strategic Recommendations
Based on these findings, we recommend the following strategic approaches for e-commerce businesses:
- Balanced Investment Strategy: Maintain investment in traditional SEO while strategically building GEO capabilities. As LaFleur Marketing notes, “Traditional SEO is not dead, but brands must now balance traditional SEO tactics with generative engine optimization (GEO) strategies.” [1]
- Authority-First Approach: Focus on building genuine authority and expertise rather than technical tricks or shortcuts. “Success in the generative era isn’t about hacking the latest algorithm. It’s about building systems that humans and machines respect. To win: Earn, don’t assume, authority; Demonstrate, don’t just claim, expertise; Structure content for machines and readers; Cultivate trust before the first click.” [1]
- Multi-Platform Strategy: Develop content strategies tailored to different AI platforms while maintaining consistent entity information across all channels. “Brand visibility in AI-generated responses depends on establishing a strong digital presence across multiple platforms.” [28]
- Technical Foundation: Ensure your technical infrastructure supports AI crawler accessibility, with particular attention to server-side rendering, structured data implementation, and proper handling of JavaScript-dependent content.
- Measurement Evolution: Implement specialized analytics for tracking AI platform interactions, combining server-level tracking with custom attribution models to understand the full impact of GEO initiatives.
- Ethical Implementation: Adhere to emerging regulatory standards for AI content transparency and disclosure, particularly as regulatory frameworks continue to evolve in major markets.
- Future Readiness: Prepare for emerging technologies like agentic browsing, multimodal AI, and extended reality integration that will further transform how users discover and interact with content.
Final Perspective
The evolution from SEO to GEO represents one of the most significant shifts in digital marketing since the rise of social media. As Orange 142 observes, “The brands that succeed in the new landscape will be those that master GEO early, especially as organic traffic continues to decline and zero-click searches become the norm.” [14]
This transition requires not just technical adaptation but a fundamental rethinking of how brands create, structure, and distribute content online. Organizations that approach GEO strategically—focusing on providing genuine value, clear information, and authoritative expertise—will be best positioned to thrive in this new AI-driven search ecosystem.
As we look toward 2026 and beyond, the convergence of GEO with other emerging technologies like AR/VR, voice commerce, and smart devices will create new challenges and opportunities. Businesses that establish strong GEO foundations now will be better equipped to adapt to these future developments and maintain visibility in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
The future of search is conversational, contextual, and increasingly AI-mediated. By embracing GEO strategies today, e-commerce businesses can ensure they remain visible, relevant, and competitive in this rapidly evolving environment.
[1] LaFleur Marketing, “Generative search optimization in 2025: What the data says (and what smart brands are doing about it)”, April 29, 2025, https://lafleur.marketing/blog/generative-search-optimization-in-2025-what-the-data-says-and-what-smart-brands-are-doing-about-it/
[3] Search Engine Land, “Google’s search market share drops below 90% for first time since 2015”, January 13, 2025, https://searchengineland.com/google-search-market-share-drops-2024-450497
[4] Microsoft, “How real-world businesses are transforming with AI — with 261 new customer stories”, April 22, 2025, https://blogs.microsoft.com/blog/2025/04/22/https-blogs-microsoft-com-blog-2024-11-12-how-real-world-businesses-are-transforming-with-ai/
[5] Coalition Technologies, “Google AI in 2025: How Search Is Changing”, May 2025, https://coalitiontechnologies.com/blog/google-ai-in-2025-how-search-is-changing
[6] Google, “Expanding AI Overviews and introducing AI Mode”, March 05, 2025, https://blog.google/products/search/ai-mode-search/
[7] ContentGrip, “How Gemini 2.0 will change the game for SEO in 2025”, December 2024, https://www.contentgrip.com/how-gemini-2-0-will-change-the-game-for-seo-in-2025/
[8] Designveloper, “Gemini vs ChatGPT: The Key Differences in 2025”, February 17, 2025, https://www.designveloper.com/blog/gemini-vs-chatgpt/
[9] NoGood, “Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Strategies to Boost AI Search Visibility”, March 21, 2025, https://nogood.io/2025/03/21/generative-engine-optimization/
[10] Connected Markets, Inc., “Generative Engine Optimization for Brands”, February 24, 2025, https://www.connectedmarkets.com/why-generative-engine-optimization-is-critical-for-saas-e-commerce-and-service-brands/
[11] Agital, “The Top 4 Metrics That Matter Most for Ecommerce Growth in 2025”, February 2025, https://agital.com/blog/top-4-metrics-for-ecommerce-growth-in-2025/
[12] API4AI, “Top AI Trends for Online Retail Businesses in 2025”, January 17, 2025, https://medium.com/@API4AI/top-ai-trends-for-online-retail-businesses-in-2025-bed9d4edeb87
[13] ToTheWeb, “GEO: The Complete Guide to AI-First Content Optimization 2025”, 2024/2025, https://totheweb.com/blog/beyond-seo-your-geo-checklist-mastering-content-creation-for-ai-search-engines/
[14] Orange 142, “GEO Best Practices Guide”, 2025, https://orange142.com/blog/geo-best-practices-guide
[15] Convert, “The Complete Guide to Optimizing Your Content For AI Search”, April 30, 2025, https://www.convert.com/blog/growth-marketing/how-to-optimize-content-for-generative-ai/
[16] First Page Sage, “Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Strategy Guide”, March 12, 2025, https://firstpagesage.com/seo-blog/generative-engine-optimization-geo-strategy-guide/
[17] Growth Marketing Pro, “What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and the 9 Ways to Do It”, March 26, 2025, https://www.growthmarketingpro.com/what-is-generative-engine-optimization-geo-and-how-to-do-it/
[18] Retail TouchPoints, “Generative AI in Retail: 4 Predictions for 2025”, February 4, 2025, https://www.retailtouchpoints.com/features/executive-viewpoints/generative-ai-in-retail-4-predictions-for-2025
[19] PixelCrayons, “What is GEO and Why It Is Important in 2025? In May 2025”, May 2025, https://www.pixelcrayons.com/blog/digital-marketing/what-is-geo-importance/
[20] Hire a Writer, “How to Track Your Brand’s Visibility Across AI Platforms”, April 14, 2025, https://www.hireawriter.us/seo/how-to-track-your-brands-visibility-across-ai-platforms
[21] Improvado, “Marketing Attribution Models: Ultimate Guide 2025”, 2025, https://improvado.io/blog/marketing-attribution-models
[23] Schema.org, “Schema.org extensions”, https://schema.org/docs/extension.html
[24] Momentic Marketing, “List of Top AI Search Crawlers + User Agents (April 2025)”, April 29, 2025, https://momenticmarketing.com/blog/ai-search-crawlers-bots
[25] Schema App, “The Semantic Value of Schema Markup in 2025”, March 18, 2025, https://www.schemaapp.com/schema-markup/the-semantic-value-of-schema-markup-in-2025/
[26] SEOMator, “AI Search Optimization in 2025: Insights from 41M Results Across ChatGPT and Google”, May 2025, https://seomator.com/blog/ai-search-optimization-insights
[27] Writesonic, “Track Traffic from ChatGPT, Gemini & Perplexity”, March 06, 2025, https://writesonic.com/blog/introducing-ai-traffic-analytics-track-chatgpt-gemini
[28] Olaf Kopp, “How to optimize for Google AIOverviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity and LLMs”, April 2025, https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-optimize-google-aioverviews-chatgpt-perplexity-llms-kopp–ikxce
[29] Salesforce, “Generative AI Regulations: What You Need To Know for 2025”, May 2025, https://www.salesforce.com/blog/generative-ai-regulations/
[30] Hyperight, “Guide to Navigating AI Regulations in 2025”, March 2025, https://hyperight.com/guide-to-navigating-ai-regulations-in-2025-6-predictions-and-strategies-for-compliance/
[31] Upvoty, “Transparency in AI-Generated Content: Disclosure and Labeling Practices”, October 2, 2024, https://www.upvoty.com/blog/transparency-in-ai-generated-content-disclosure-and-labeling-practices
[32] Pillsbury Law, “California’s AI Laws Are Here—Is Your Business Ready?”, February 7, 2025, https://www.pillsburylaw.com/en/news-and-insights/california-ai-laws.html
[33] Coupler.io, “How to Track and Analyze AI Traffic”, May 2025, https://blog.coupler.io/how-to-track-and-analyze-ai-traffic/
[34] Search Engine Journal, “Q2 SEO & AI Update: How To Track & Optimize AI Search Performance”, March 27, 2025, https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/q2-seo-ai-update-how-to-track-optimize-ai-search-performance-ab3d/277246357
[35] Empathy First Media, “AI Analytics & Performance Reporting Trends May 2025”, April 28, 2025, https://empathyfirstmedia.com/ai-analytics-performance-reporting-trends-may-2025/
[36] Improvado, “How to Build a Custom Marketing Attribution Model [Guide]”, May 2025, https://improvado.io/blog/how-to-create-your-own-attribution-model
[37] The Future of Commerce, “E-commerce trends 2025: Top 10 insights and stats driving online shopping as AI goes mainstream”, December 4, 2024, https://www.the-future-of-commerce.com/2024/12/04/e-commerce-trends-2025/
[38] ShipperHQ, “Voice Commerce, AI and AR: How Tech is Changing Ecommerce”, April 2021, https://blog.shipperhq.com/2021/04/voice-commerce-ai-ar
[39] MDPI, “Technology Development in Online Grocery Shopping—From Shopping Services to Virtual Reality, Metaverse, and Smart Devices: A Review”, December 8, 2024, https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/13/23/3959
[40] Signifyd, “2025 Ecommerce Trends and Predictions”, November 11, 2024, https://www.signifyd.com/blog/2025-retail-ecommerce-predictions/
[41] Mercatus, “The Year in Grocery Trends: 5 Essential Lessons for Grocers in 2025”, December 30, 2024, https://www.mercatus.com/blog/the-year-in-grocery-trends-5-essential-lessons-for-grocers-in-2025/
[42] Brick Meets Click, “March 2025 eGrocery Surges to $9.7 Billion – Brick Meets Click”, April 10, 2025, https://www.brickmeetsclick.com/insights/march-2025-egrocery-surges-to-9-7-billion-what-it-means-for-competing-online
[43] Uxify, “Top 11 AI trends shaping Ecommerce in 2025 to boost sales”, May 2025, https://uxify.com/blog/post/ai-ecommerce-trends